Photo by Wyxina Tresse on Unsplash
Web 5.0: A Beginners Guide To Understanding The New Internet Frontier
A simple guide to understanding the evolution and new concept of the web.
Introduction
If you asked me about the most remarkable invention, I'd tell you the Internet. Of course, you might have contradictory perspectives which are also valid. But why do I think the Internet is humanity's greatest invention? My answer is simple: the Internet has given us more freedom and autonomy and increased trade, learning, and interaction across continents, cultures, and tribes. Think about it: with the click of a few keys, you can sell your skills, learn about cultures, make new friends, and become part of a community. But that's me.
Although this democratization and autonomy has had a few roadblocks, the Internet is also rapidly evolving towards democratization by placing more power in the hands of users. Since the Internet was introduced into the world in 1993, it has constantly undergone developments that have influenced various fields. Since its inception, the Internet has transitioned through several phases in several decades. It continues to evolve as new phases of innovation.
If you're like most people, you may still be discovering the concept of Web 3.0 and might receive a more advanced Web 5.0 as a shocker (I was, too). You read that right: the World Wide Web has evolved into a Web 5.0. If you're hearing about this concept for the first time, here's a quick summary: Web 5.0 gives users control over their personal data and identity in ways previous web models could not.
In this article, I take you through the concept of Web 5.0 as explained in this The Block Head (TBD) workshop.
Evolution of The Internet

Before we dive into Web 5.0 technology and the potential this will have on users and innovation in general, let's understand the historical evolution of the World Wide Web and how we got here.
Web 1.0 - The Static Web
What is Web 1.0? Also called the static web, web 1.0 focused more on read-only applications. Think of Web 1.0 as the digital Wild West. It was a time when the Internet was a static HTML page, and the most exciting thing you could do was read information. Interactivity? Not so much.
Web 2.0 - The Interactive Playground
Then came Web 2.0, the era of interaction. Web 2.0 shifted the earlier dynamics from read-only to read-and-write. With Web 2.0, you can now interact with other internet users. Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter entered the scene, and suddenly, the Internet became a space where you could create content, share it, and connect with people worldwide.
Web 3.0 - The Semantic Web
Web 3.0 took things up a notch. Imagine a web that understands you. This is the semantic web, where machines learn to interpret data. Web 3.0 brings together integration, data, automation, and discovery, all while embracing the trends of a more connected world and increased mobility. It harnesses the strength of decentralization to provide the best aspects of AI (Artificial Intelligence), machine learning, and 3D computing in a more advanced internet experience. Search engines became smarter, providing more relevant results, and the Internet started to grasp the context of your queries.
What's Web 4.0?
Web 4.0 is often skipped in conversations. Web 4.0 relies on functionality and applies wireless communication to increase connectivity between people and other connected objects in physical and virtual worlds. Some consider it an extension of Web 3.0, while others believe it's the precursor to what we're diving into – Web 5.0. Some enthusiasts have also called it the symbiotic web, a symbiosis between humans and computers.
WHAT IS WEB 5.0
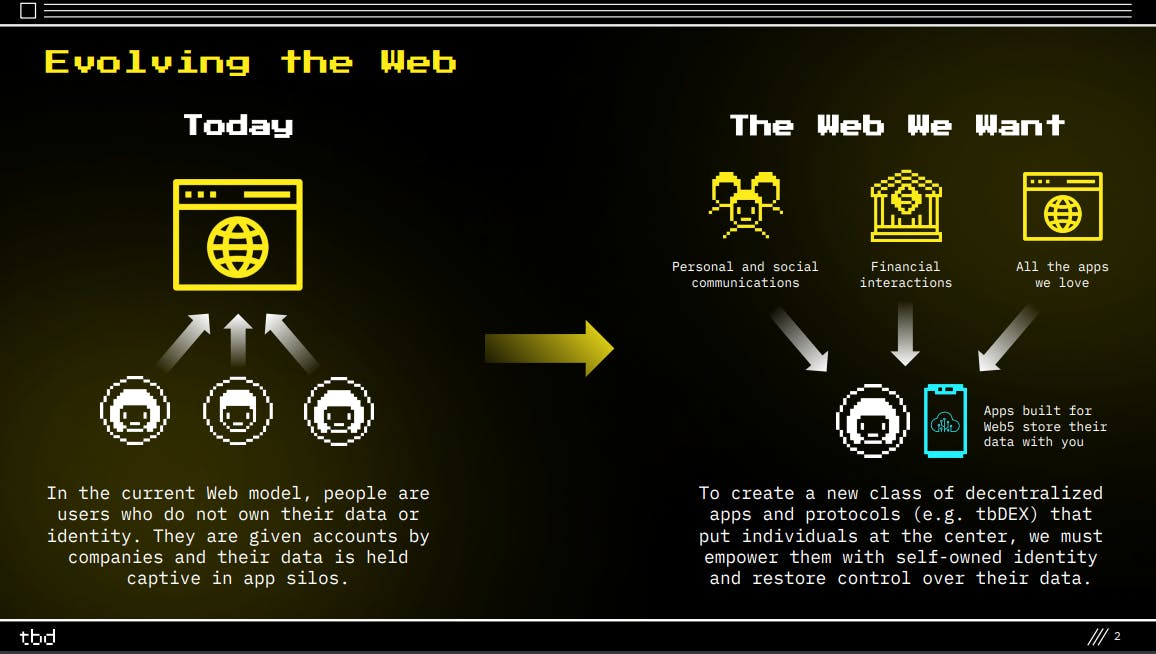
Now, imagine an internet where you have complete control over your data, privacy, and identity compared to previous web concepts, which put your personal data in the hands of third-party companies. With such a concept, you get less unrequested ads, own your content, and the security that these companies don't use your data as they wish. Now that's democratization; that is web 5.0.
So, what is Web 5? TBD describes Web 5 as an evolution of the web that enables decentralized apps and protocols that put users in control of their data.
Web5 operates on a simple yet powerful idea: giving you control over your data and identity. It advocates for total decentralization, meaning you own where your personal data is stored on the Internet. But what does decentralization really mean?
The Oxford Dictionary defines decentralization as the transfer of control from one central authority to multiple local offices or authorities. Currently, when we use the Internet or participate in social media activities, our data, identity, and online interactions are stored in one central place controlled by a single company or organization. This gives them complete control over our data and the ability to use it as they see fit.
Decentralization, on the other hand, flips the script. Your data is stored across various networks, utilizing technologies like Bitcoin with cryptographic and encryption security measures to keep your information completely safe. While Web3 allows decentralization and anonymity online, it doesn't completely control your data and private information. This is the problem that Web5 aims to solve.
Web5 envisions a decentralized internet similar to Web3 but with a critical distinction. In Web5, users store their personal information. They can decide who can access it, allowing them to revoke access anytime.

Simply put, Web5 combines the best of both worlds – the user-friendly convenience of Web 2.0 and the decentralization principles of Web3. It takes the decentralization technology offered by Web3. It applies to our familiar applications and platforms in our everyday Web 2.0 experiences. In other words, Web2 + Web3 = Web5. It's about creating a more user-centric and secure internet where individuals have the ultimate say over their data.
Pillars Of Web 5.0
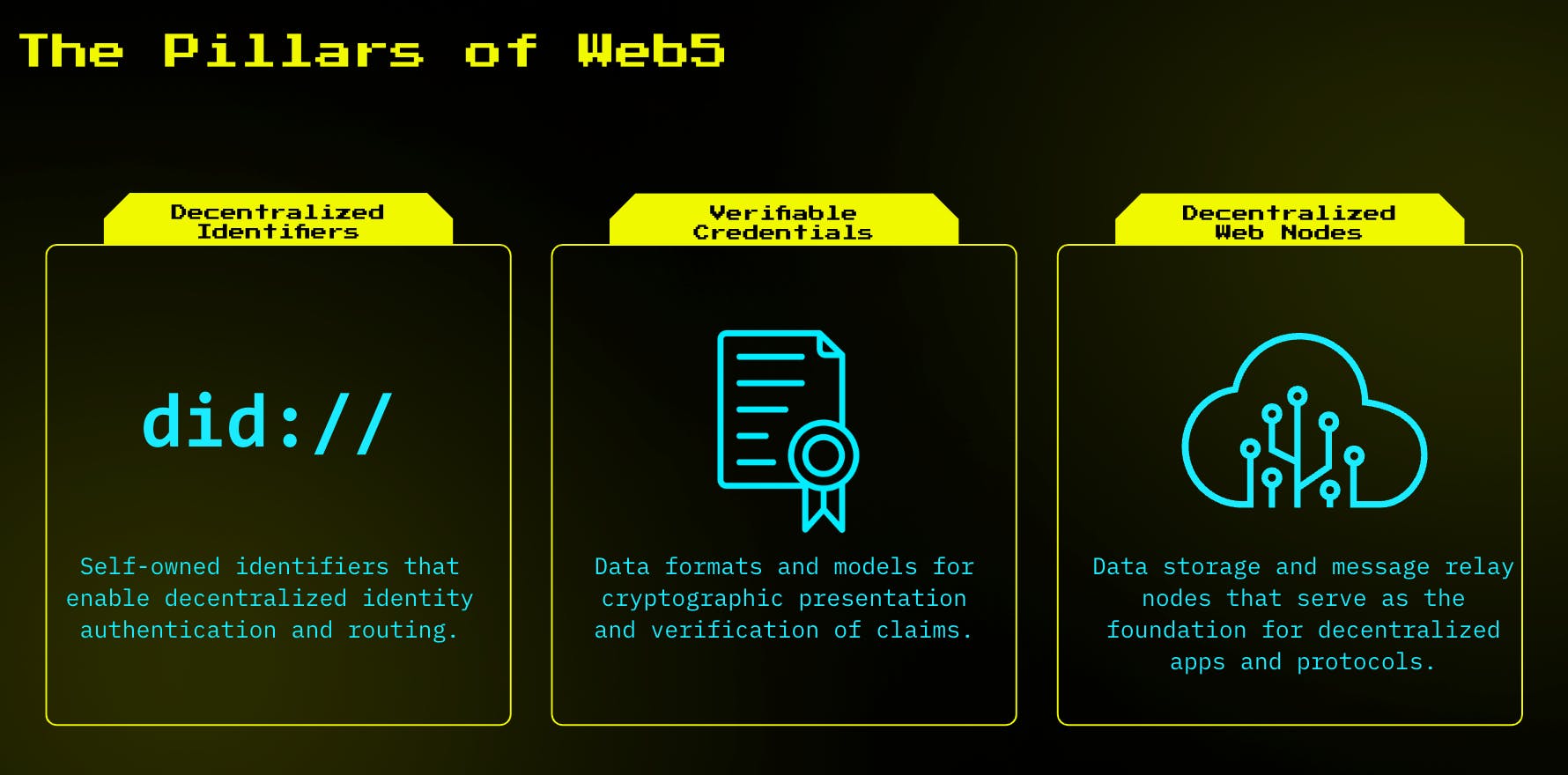
To accomplish the objectives of Web 5.0, the TBD is building Web 5.0 technology on three new identity standards already established by the Worldwide Web Consortium. Without diving into the technical jargon and complexity, I'll simply summarize the three pillars of web5 technology.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) in Web5 are like the IP addresses of this new internet era. They're self-generated and not controlled by any central authority. The network indexes these identifiers, and users can discover and verify them independently. With a DID, you wouldn't need to remember your username and password for every application you use, as this serves as a one-stop for all your credentials.

Verifiable credentials
Verifiable credentials are a trust-building tool among users. They involve data formats and models for cryptographically presenting and verifying claims, enhancing trust in online interactions.
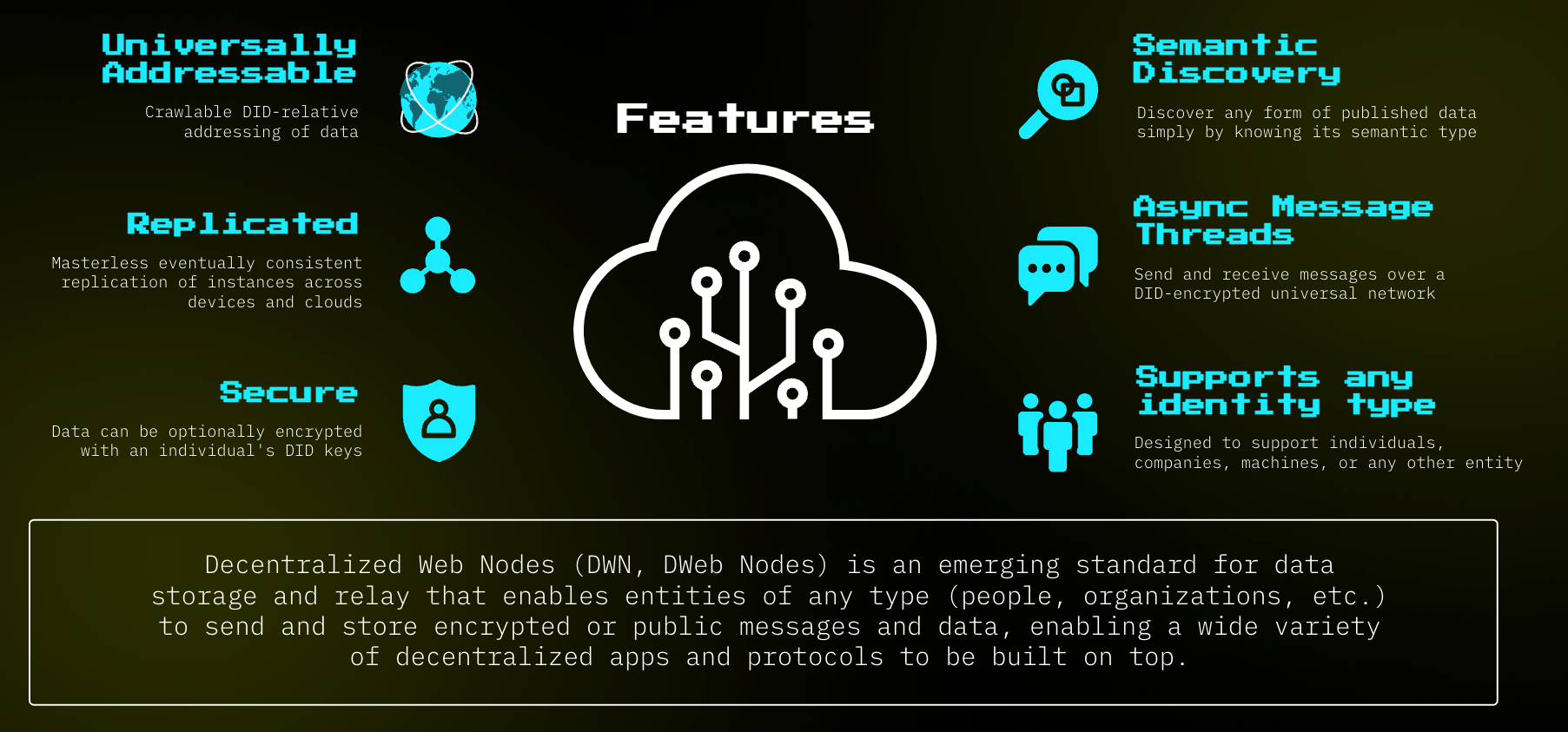
Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs)
Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) are the backbone of Web5's data storage and relay system. It's like your personal Dropbox, but without third-party oversight where your data is accessible or the terms of service can change according to company policy. They allow any entity, whether a person or an organization, to send and store encrypted or public messages and data. This enables the creation of various decentralized apps and protocols on the Web5 platform.
This approach aims to tackle some of the challenges faced by Web3, offering a more promising direction for the future.
How Does It Work?
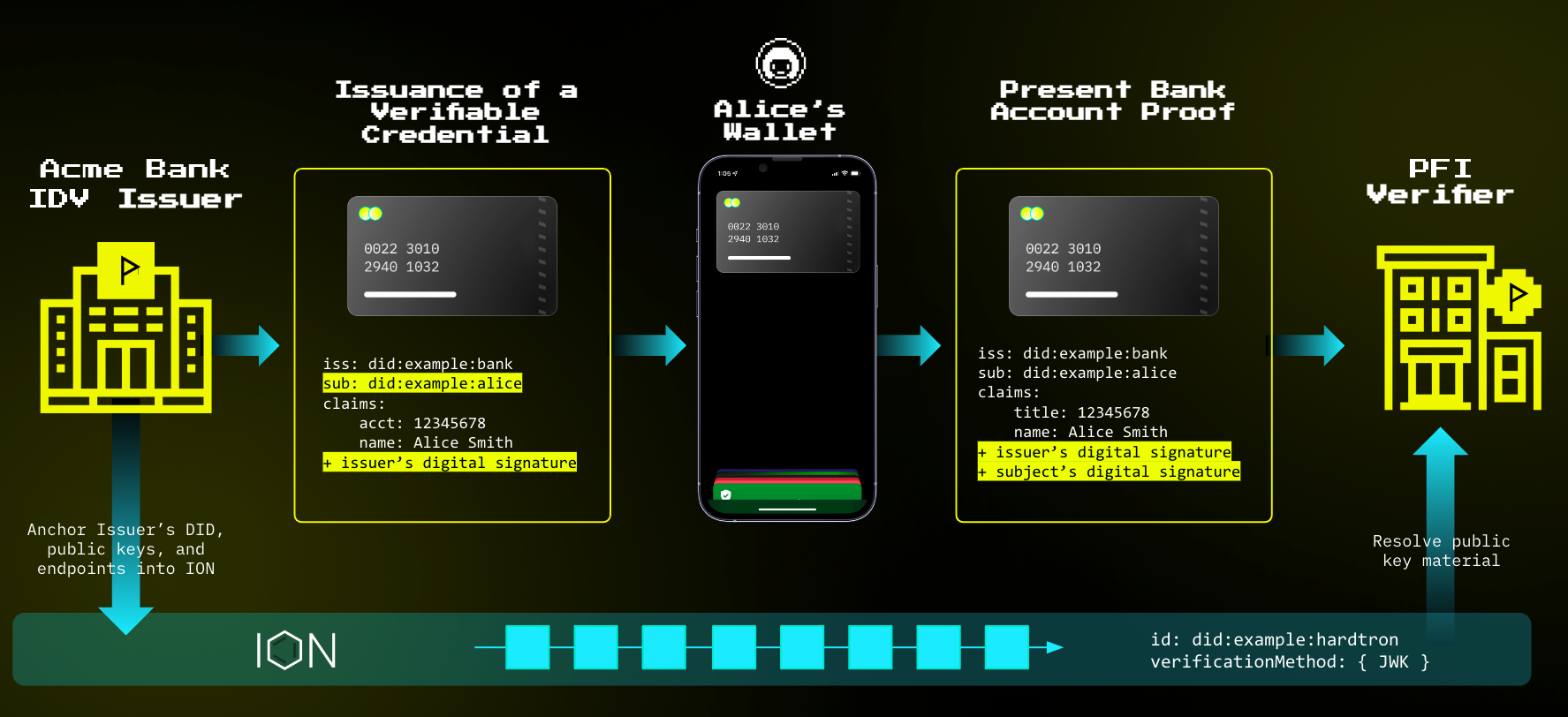
Web5 empowers you to store and manage your data using decentralized web nodes. Unlike Web3, Web5 doesn't rely on smart contracts or tokens. Imagine having a secure box where you keep all your info – username, password, email, health records, and more. This data is stored locally but also across decentralized web nodes. When signing up for a website, you choose what data to share, retaining the ability to revoke access anytime. Your data is encrypted, ensuring anonymity and control.
A digital identity wallet lets you create a digital identity or receive verifiable credentials from trusted sources. Whether it's passports or licenses, you hold these credentials. When needed, you can present them to a Verifier. The Verifier checks the credentials against your Digital ID (DID) and trusts the issuer's DID. If all checks out, they trust that you have the qualifications presented.
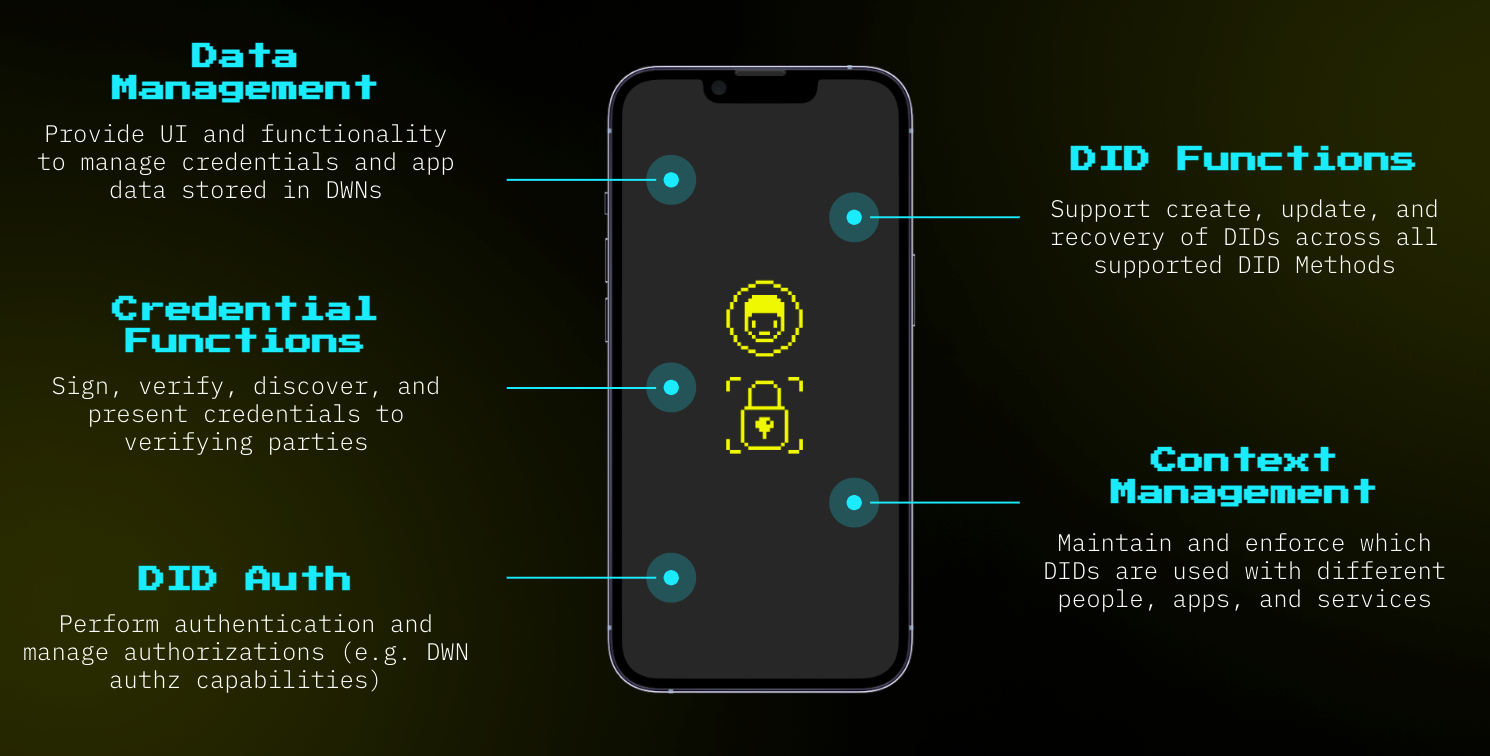
But What Was Wrong with Web 3.0?
Jack Dorsey, the former CEO of Twitter, criticized the global implementation of Web 3.0, stating that decentralization in the Semantic Web is a myth due to control retained by nodes in a blockchain network. Identifying these limitations, Jack introduced the Web 5.0 project, gaining attention from experts. Jack envisions Web 5.0 as an internet version promoting free expression and user data control. He assigned management of the project to the Bitcoin unit of Block Inc., his financial company, signalling a more indepth evolution beyond mere blockchain implementation.
But Jack isn't the only internet mogul who thinks we need a more decentralized, democratic internet. Tim Burners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, is also working on a similar decentralized internet. His reason is that his initial intention for the Internet was to be decentralized, and he's quoted saying,
I think the public has been concerned about privacy—the fact that these platforms have a vast amount of data, and they abuse it. But I think what they're missing sometimes is the lack of empowerment. You need to get back to a situation where you have autonomy and control of your data.
Features Of Web 5.0
With this understanding of Web 5 technology, what difference does it make? What are the features and potential uses of Web 5?
First, let's explore the features:
Identity Control
Web 5.0 puts users in charge of their identity. It introduces a decentralized platform where users can securely store credentials from other platforms. Notably, only users have control over this storage, ensuring that no user identity data is collected by the Internet. This means you can own and personalize your internet experiences and identity, not what's handed down.
Data Ownership
Through complete decentralization, Web 5.0 gives users full ownership of their data. You can choose what information to share with companies and what to keep private. Users have their own blockchain participation, offering a secure singular place to store their data.
Use Cases for Applicability
It goes without saying that technology is only innovative if it's applicable and scalable. This is no different for Web 5. So, where is this exciting concept of Web 5 usable?
(1) Private Social Networks: With SSI, social media has become more privacy-friendly. You get to control your data securely, ensuring your connections and interactions are kept private.
(2) Healthcare You Can Trust: In Web5, healthcare gets a privacy boost. Patient data is handled with utmost security, ensuring it's saved, shared, and managed with integrity.
(3) Take Charge of Your Finances: Web3 introduced Decentralized Finance (DeFi) on the blockchain. Now, Web5 goes a step further, giving you more control over financial transactions by letting you manage your identity the way you want.
(4) Fast and Secure Credential Verification: Web5 brings a speedy and secure way to verify credentials. No more waiting – it's quicker than using a password manager.
(5) Safe Communication Apps: Communication apps on Web5 prioritize your privacy and security. Say goodbye to concerns about your messages and calls being secure.
(6) Securing IoT Devices: Web5 ensures that Internet of Things (IoT) devices are managed securely. They focus on privacy, preventing data breaches, and protecting your IoT interactions.
Conclusion
As I stated earlier, I am a big fan of the Internet, and this new evolution and transition into a more democratized web is exciting. This is an essential phase in the development of the internet and would completely transform our experiences. The possibilities are endless when you pause to imagine how much this innovation will improve and impact the human experience. As a product designer, I can't wait to see and apply these developments to better user experience.
For more on Web 5.0 and to see what TBD building is, you can use these links.